Uncovering a root cause of the Growing Concern
A growing
concern
Genetic variants in the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) pathway can impair the regulation of hunger, food intake, satiety and energy expenditure.1,2
Melanocortin-4 receptor & obesity
Impaired MC4R signalling can lead to hyperphagia (pathological, insatiable hunger) and early-onset obesity, regardless of environmental and lifestyle factors.3,4
There are over 113 genes with potential ties to the MC4R pathway; and rare genetic variants within the MC4R pathway may result in impaired neuronal signalling, leading to rare genetic diseases such as pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) deficiency obesity and leptin receptor (LEPR) deficiency obesity.4,5
Undiagnosed root cause
A root cause of early-onset obesity is often underdiagnosed. Proactive identification of cardinal symptoms can help move children living with a rare MC4R pathway disease onto their appropriate care path.4,6
Got a specific question?
If you can't find what you're looking for, or want to discuss a topic in more detail, reach out to our team.
Proactive, personalised obesity management
Prof. Luca Busetto discusses the need for proactive obesity management, identifying a root cause of obesity and treating in a personalised way.
Rhythm Pharmaceuticals is leveraging a IQVIA's Healthcare Professional Authentication solution to identify your eligibility to access this video content. If you already have an IQVIA account using it with other healthcare providers, please click 'Login' otherwise click 'Signup'.
Identifying a rare MC4R pathway disease
Once the cardinal symptoms of hyperphagia and early-onset obesity have been identified, genetic screening can help to identify the presence of a rare MC4R pathway disease.7
When considering whether your patients should be evaluated for a rare MC4R pathway disease, think of the following cardinal symptoms:8

Heightened and prolonged hunger

Shorter duration of satiety

Severe preoccupation with food

Longer time to reach satiety

Significant stress and inappropriate response if denied food

Excessive food behaviours (night eating, stealing food, foraging for food in the garbage)
Early-onset obesity (early-onset is typically before 5 years of age)4,9,10
A BMI curve well above reference percentiles may indicate an underlying rare MC4R pathway disease
Learn about treatment
For patients with genetic obesity, time is ticking


Speeding up referral
There are a few vital clinical investigations to undertake for the prompt identification of rare MC4R pathway diseases:11
- Taking a detailed clinical history is critical
- Record family history, if available
Previous resistance to traditional obesity management strategies may be a valuable measure to assess.
While individual variants are uncommon, rare MC4R pathway diseases are likely not uncommon among people with early-onset, severe obesity. The age of obesity onset is a key factor in selecting patients with potential variants in obesity-associated genes.4,6
01
— 03
Content Hub
Click here to find additional information on rare MC4R pathway diseases as well as educational resources and meetings produced by Rhythm.
We will continue to update this page with resources about monogenic obesity as well as other rare diseases of the MC4R pathway.
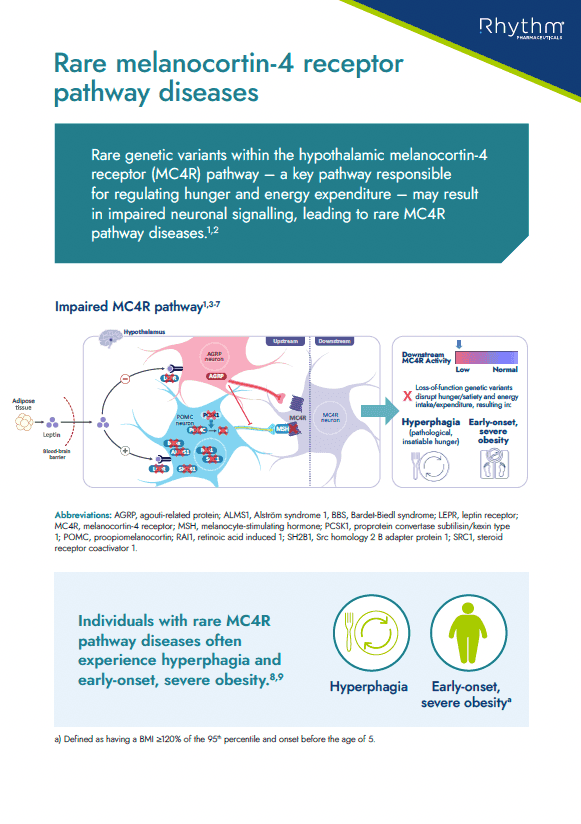
Educational information on rare MC4R pathway diseases and how they can lead to hyperphagia and early-onset obesity
Handout
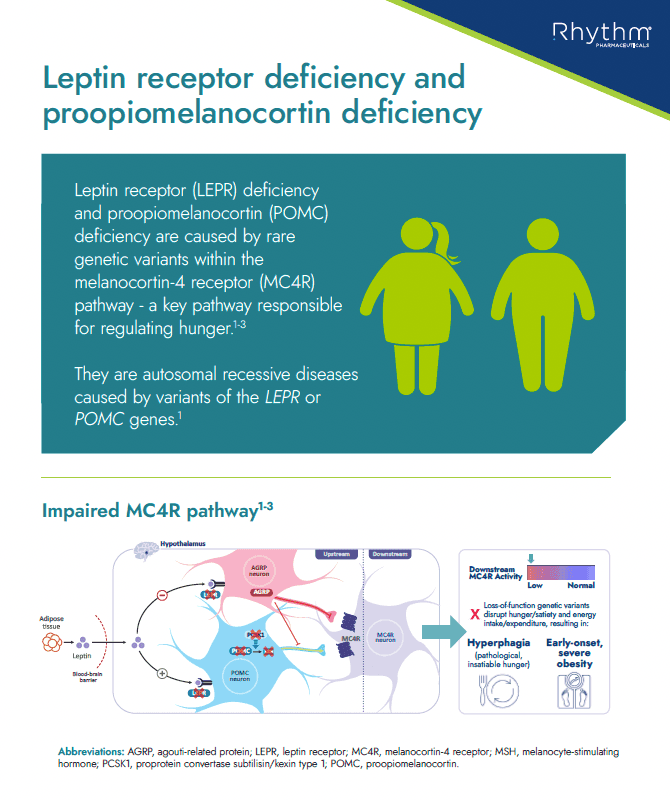
Educational information about LEPR and POMC deficiency, including what it is, key characteristics/clinical features in patients with these conditions, prevalence and route to diagnosis
Handout
References:
- 1. Yazdi FT, et al. PeerJ. 2015;3:e856.
- 2. Acosta A, et al. Genes Nutr. 2014;9:384.
- 3. Haqq AM, et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(12):859–868.
- 4. Huvenne H, et al. Obes Facts. 2016;9:158–73
- 5. Fonseca ACP, et al. J Diabetes Complications. 2017;31:1549–1561.
- 6. Clément K, et al. Physiology Behavior. 2020;227:113134.
- 7. Styne DM, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102:709–757.
- 8. Heymsfield SB, et al. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22:S1‒S17.
- 9. Ellacott KLJ & Cone RD. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2006;361:1265–74.
- 10. Kohldorf K, et al. Int J Obes (Lond). 2018;42:1602–1609.
- 11. August GP, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:4576–99.
- 12. Kleinendorst L, et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017:bcr2017221067.